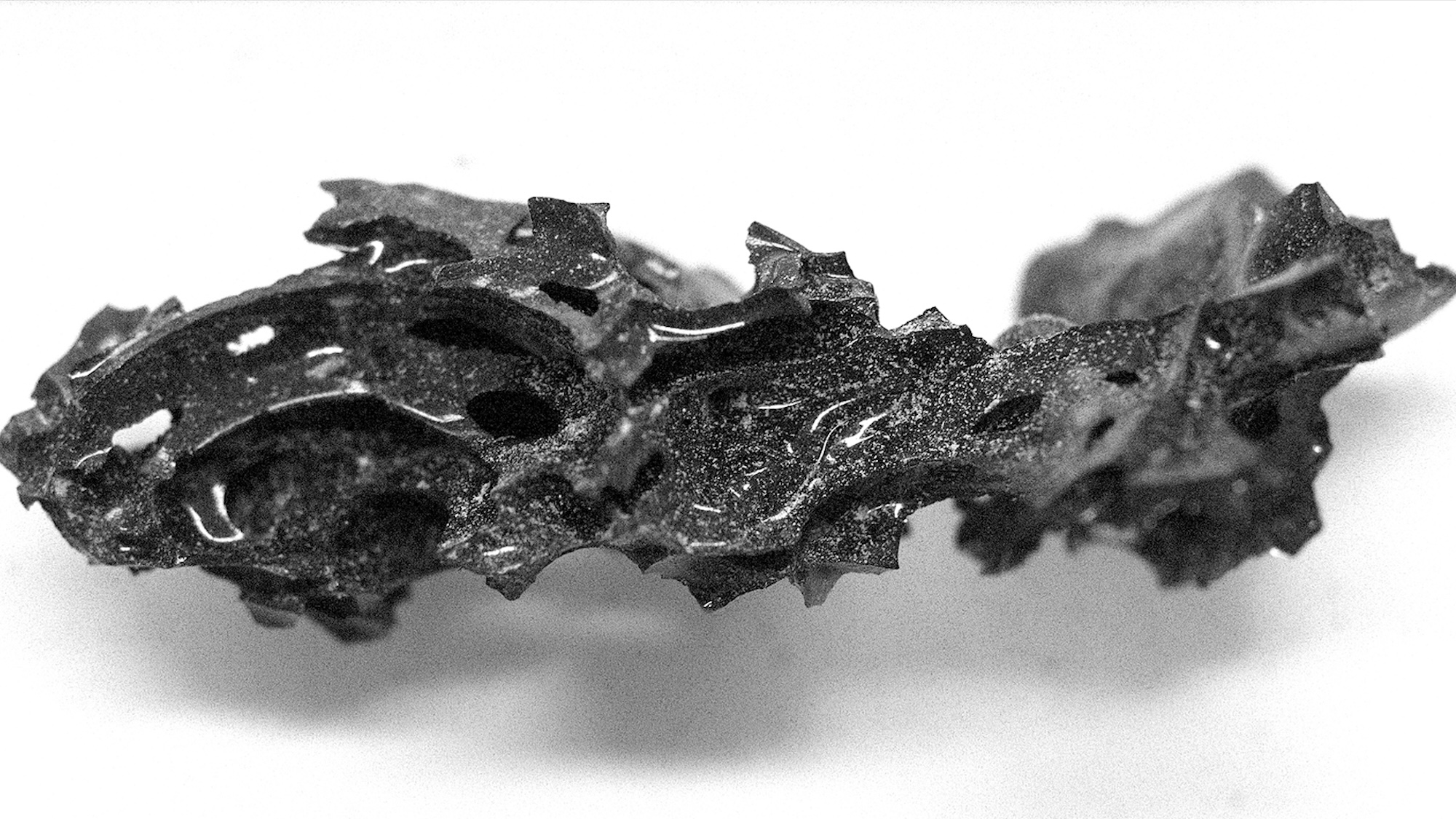
The eruption of Mount Vesuvius in 79 CE presented its surrounding ancient Roman communities with a number of terrifying ways to die: falling debris, collapsing buildings, asphyxiation from superheated dust plumes, etc.. And while attention is often focused on the destruction of Pompeii and its thousands of victims, the fate of nearby Herculaneum wasn’t much better. According to recent analysis of unique samples recovered from the seaside archeological site, the Vesuvius eruption even caused one person’s brain to flash-fry into a rare form of organic glass.
The theory, laid out in a study published February 27 in the journal Scientific Reports, is based on examinations of tiny shards found in 2020 inside the skull and spinal column of an individual at Herculaneum–a small port town with a population of around 5,000 people at the time. The victim is believed to have been a roughly 20-year-old man who worked as a guard at the Collegium Augustalium, a public building dedicated to worshipping Emperor Augustus. At the time of his death, however, the guard was laying in his bed—and it was this environment that likely fostered the extremely specific conditions needed for brain and spinal fluid vitrification.